Ever experienced the frustration of a dead headlight, a malfunctioning radio, or a mysteriously inoperative windshield wiper? These common automotive hiccups can often be traced back to a single culprit: a blown fuse. You might be wondering, “What in the world is a fuse, and how do I even begin to tackle this electrical puzzle?” Fear not, dear driver, for the 2003 Ford Focus fuse box diagram holds the key to conquering these electrical woes.
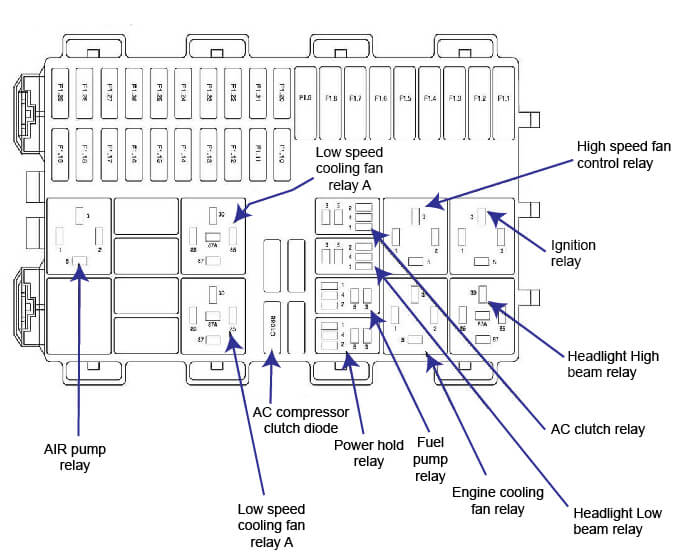
Image: mydiagram.online
This guide delves into the intricacies of the 2003 Ford Focus fuse box diagram, unraveling the mysteries of electrical circuits and empowering you to become a master of your vehicle’s electrical system. We’ll explore the types of fuses, their locations, and the crucial role they play in protecting your car’s electrical components. Get ready to become a fuse-box wizard, ready to tackle any electrical challenge that comes your way.
Understanding the Fuse Box: Your Car’s Electrical Guardian
In the world of automotive electrical systems, fuses are the silent heroes, silently safeguarding your car’s components from the potentially devastating effects of electrical overload. Think of them as tiny warriors, standing guard against electrical surges and short circuits. When a fuse blows, it effectively breaks the electrical circuit, preventing damage to your valuable car parts.
Types of Fuses: A Symphony of Protection
The 2003 Ford Focus employs a range of fuse types, each serving a specific purpose. Let’s delve into these unsung heroes:
- Blade Fuses: These slender, rectangular fuses are ubiquitous in modern cars. They are generally rated in amps (A), indicating the maximum electrical current they can handle before blowing.
- Mini Fuses: Similar to blade fuses, mini fuses are smaller, often found in smaller circuits like interior lights and accessories. They also feature amp ratings.
- ATC Fuses: Slightly larger than mini fuses, these are frequently found in the fuse box of the 2003 Ford Focus. They provide protection for higher-amp circuits.
Delving Deeper: The 2003 Ford Focus Fuse Box Diagram
To navigate the world of fuses effectively, you need a map – that map is the 2003 Ford Focus fuse box diagram. This diagram serves as your guide to the fuse box labyrinth, providing detailed information about each fuse, its purpose, and its corresponding circuit. Armed with this diagram, you can confidently diagnose electrical malfunctions and replace blown fuses.

Image: www.mikrora.com
Decoding the Diagram: Unveiling the Electrical Blueprint
The 2003 Ford Focus fuse box diagram is usually found in your owner’s manual or can be easily accessed online.
Here’s what you’ll typically find on the diagram:
- Fuse Locations: The diagram visually depicts the layout of the fuse box, with each fuse positioned according to its location in the box.
- Fuse Numbers: Each fuse is designated with a unique number, making it easy to identify and locate.
- Amp Ratings: The diagram specifies the amp rating of each fuse, crucial for replacing a blown fuse with the correct replacement.
- Circuit Descriptions: The diagram clearly indicates which component or system each fuse protects, allowing you to pinpoint the source of an electrical problem.
The Art of Replacing a Blown Fuse
Armed with your trusty fuse box diagram, you’re now ready to tackle the task of replacing a blown fuse. But before you dive in, there are a few key steps to follow:
Steps to Fuse Replacement
- Locate the Fuse Box: In the 2003 Ford Focus, the fuse box is typically located in the engine compartment, either on the driver’s side or passenger’s side. Your owner’s manual will confirm the exact location.
- Identify the Blown Fuse: Inspect the fuse box for fuses that appear damaged or broken. A blown fuse might be discolored, melted, or have a visible break in the wire.
- Consult the Diagram: Use the fuse box diagram to determine the amp rating and circuit for the blown fuse.
- Replace the Fuse: Use a pair of tweezers or pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse. Replace it with a new fuse of the same amp rating. Make sure the new fuse is firmly inserted in its slot.
- Test the Circuit: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position and test the affected component to ensure the fuse replacement has successfully restored functionality.
Navigating Common Fuse Box Issues
While replacing a blown fuse is often a straightforward task, there are times when you might encounter more complex issues within the fuse box:
Unveiling Fuse Box Troubles
- Multiple Blown Fuses: If you’re encountering multiple blown fuses, this could indicate a bigger underlying issue. A short circuit within the wiring system might be the culprit. Consider taking your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for a thorough inspection.
- Fuse Box Damage: If the fuse box itself appears damaged, exhibiting signs of corrosion or melting, it’s essential to seek professional assistance. A compromised fuse box poses a safety risk and requires professional repair.
- Incorrect Fuse Replacement: Using a fuse with an improper amp rating can create a hazard. If the chosen fuse is too low in amps, it will blow repeatedly. Conversely, a fuse with a higher amp rating can fail to protect the circuit properly, potentially causing electrical damage.
Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Dive into Fuse Box Mysteries
For those seeking a more comprehensive understanding of fuse box intricacies, let’s venture into some additional points to consider:
Fuse Box Anatomy and Function
The fuse box itself is more than just a simple container. It houses a complex network of electrical connections, ensuring proper flow of current to your car’s various systems. Here are some key components you might notice inside the fuse box:
- Fuse Holders: These are the sockets that hold the individual fuses in place, ensuring secure electrical connections.
- Relay Holders: Relays are specialized electrical switches that control the flow of current to various components. Relay holders accommodate these relays within the fuse box.
- Terminal Blocks: These serve as connection points for wires, facilitating the efficient transfer of electrical signals.
Fuse Box Maintenance: Keeping Your Electrical System Healthy
Just like any other part of your car, the fuse box requires occasional care to ensure optimal performance. Here are a few maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the fuse box for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Early detection and intervention can prevent more serious issues.
- Cleanliness: Use compressed air or a soft-bristled brush to remove dust and dirt from the fuse box. Maintaining cleanliness prevents electrical problems and ensures optimal conductivity.
- Fuse Box Covers: Always ensure the fuse box cover is securely closed after accessing the fuses. This protects the system from external elements and electrical hazards.
Ford Focus 2003 Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion: Mastering the Fuse Box, Mastering Your Car
By understanding the 2003 Ford Focus fuse box diagram and armed with the knowledge of fuse types and replacement techniques, you can confidently diagnose and resolve common electrical issues. Remember, the fuse box is your vehicle’s electrical guardian, and by honing your fuse box knowledge you’ll gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s electrical system, empowering you to handle minor electrical problems with ease. So, the next time a light bulb flickers or your windshield wipers fail, banish the fear of electrical mysteries and confidently tackle the problem with your newfound fuse box expertise.




