The world of business is complex, and navigating its intricacies often requires a keen eye for detail and a commitment to ethical practices. Enter the field of auditing and assurance services, playing a vital role in providing confidence and transparency within organizations. But what are the principles that underpin these services? How do they ensure accountability and promote trust? In this article, we’ll delve into the fundamental principles of auditing and other assurance services, exploring their significance in today’s dynamic business landscape.

Image: www.slideshare.net
Imagine a scenario where you’re investing in a company, but you lack the means to verify the accuracy of its financial statements. This is where auditing comes to the rescue, providing a third-party perspective to assess the financial health of a business. Auditing services go beyond simply checking numbers; they involve a thorough analysis of financial records, internal controls, and operational processes, ensuring that financial information is presented fairly and transparently. This level of scrutiny fosters trust among stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and promoting accountability within the organization.
Understanding the Principles of Auditing and Assurance Services
The principles that guide auditing and assurance services are not merely theoretical constructs; they are the bedrock upon which these services are built. These principles ensure that the process is objective, independent, and evidence-based, allowing for the delivery of credible and reliable assurance. Whether it’s assessing financial statements, evaluating internal controls, or providing attestations on specific business processes, the guiding principles remain consistent.
Core Principles of Auditing and Assurance Services
At the heart of auditing and assurance services lie a set of core principles:
- Independence: Auditors must maintain independence both in fact and appearance, ensuring that their judgment is not compromised by personal biases or external pressures. This principle is paramount to preserving the integrity of the audit process.
- Professional Skepticism: A healthy dose of skepticism is critical in auditing. Auditors must not blindly accept management’s assertions but actively question and seek corroborating evidence for every claim.
- Due Professional Care: Auditors are expected to apply the necessary skill, care, and diligence in performing their work, adhering to professional standards and ethical guidelines.
- Objectivity: Auditors must maintain objectivity in their assessments, avoiding any bias or preconceived notions that might influence their findings.
- Professional Judgment: Auditing requires significant professional judgment in interpreting evidence, assessing risks, and forming conclusions. Auditors must exercise sound judgment based on their professional experience and expertise.
- Confidentiality: Auditors are bound by confidentiality agreements, ensuring that information obtained during the audit process is kept private and not disclosed to unauthorized parties.
These core principles form the foundation of a robust audit process, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the assurance provided. They serve as a guiding light for auditors, ensuring they act ethically, professionally, and with due care in every engagement. However, the principles themselves are not a static set of rules; they must be applied flexibly, adapting to the ever-evolving business landscape and evolving auditing standards.
The Importance of Auditing and Assurance Services
Beyond theoretical concepts, auditing and assurance services play a crucial role in the practical world of business. Their impact can be seen across numerous areas, contributing to a more transparent and accountable business environment.
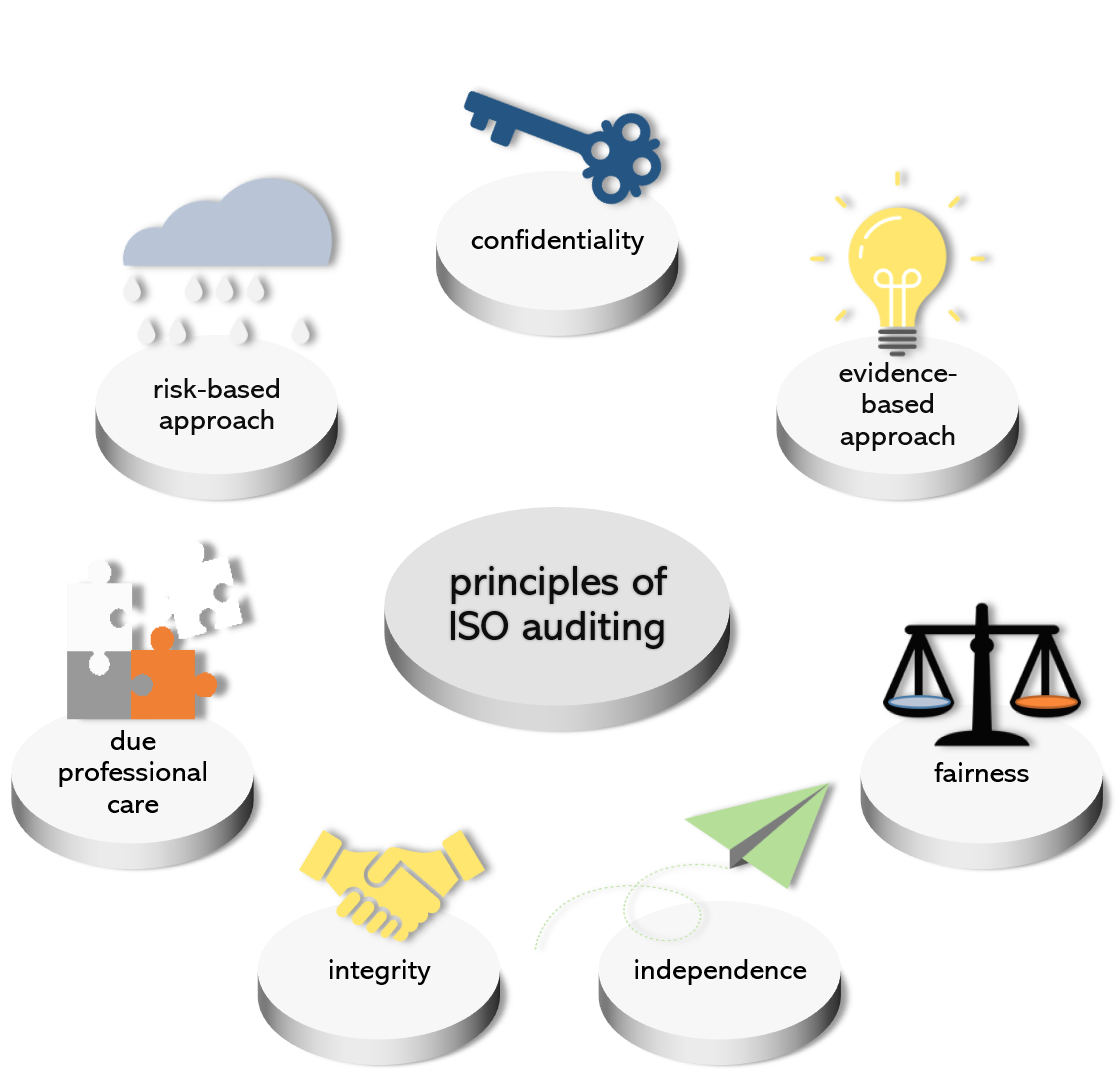
Image: www.artfulcompliance.com
Promoting Financial Transparency and Accountability
Auditing plays a vital role in promoting financial transparency and accountability. By scrutinizing financial records, internal controls, and operational processes, auditors provide stakeholders with an independent assessment of an organization’s financial health. This assurance is critical for investors, lenders, regulators, and other parties who rely on accurate financial information to make informed decisions.
Enhancing Internal Controls and Risk Management
Auditing services extend beyond financial reporting, encompassing evaluation of internal controls. Auditors assess the efficacy of internal controls, identifying weaknesses and recommending improvements. This process helps organizations strengthen their internal control framework, mitigating risks and improving operational efficiency. This can also help companies comply with regulations and minimize the risk of fraud or misconduct.
Improving Corporate Governance and Ethics
By promoting transparent and accountable practices, auditing contributes to a culture of strong corporate governance. Auditors act as independent watchdogs, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and ethical standards, holding management accountable for their actions. This fosters trust among stakeholders, facilitating sustainable growth and long-term success.
Emerging Trends and Developments in Auditing
The field of auditing is constantly evolving, adapting to new technologies, regulatory changes, and evolving business practices. Some key trends shaping the future of auditing include:
- Data Analytics: The use of data analytics is becoming increasingly prevalent in auditing. This enables auditors to analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and extract insights that can enhance their understanding of the audit subject matter.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is starting to play a role in automating certain audit tasks, such as data extraction and analysis. This can improve efficiency and free up auditors to focus on more complex and value-adding tasks.
- Cybersecurity: As cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, auditors are increasingly focusing on assessing an organization’s cybersecurity posture. This includes the adequacy of controls, the risks posed by cyberattacks, and the potential impact on financial reporting.
- Sustainability and ESG Reporting: Sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting are gaining prominence. Auditors are becoming increasingly involved in assessing an organization’s sustainability practices and providing assurance on ESG-related disclosures.
These trends are reshaping the landscape of auditing, creating new opportunities for auditors to leverage technology and data to provide even more meaningful and impactful assurance. As new technologies and trends emerge, auditors must constantly adapt and develop their skills to remain relevant and effective.
Tips and Expert Advice for Navigating Auditing and Assurance Services
Understanding the principles of auditing and assurance services is essential for any business professional. Here are some tips and expert advice for navigating this complex landscape:
- Engage with a Qualified Auditor: Partnering with a reputable and qualified auditor is crucial. Ensure they possess the necessary expertise, experience, and qualifications to provide valuable insights and assurance.
- Understand Your Responsibilities: Management and those responsible for financial reporting have significant responsibilities in the audit process. Ensure a clear understanding of your role and obligations, actively engaging with the auditor and providing transparent and timely information.
- Embrace the Audit Process: Instead of viewing auditing as an adversarial process, embrace it as an opportunity to learn and improve. Work collaboratively with your auditor to enhance internal controls, mitigate risks, and improve overall business operations.
- Stay Informed on Latest Trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in auditing, including emerging trends, technologies, and regulatory changes. This will help you understand the evolving landscape and prepare for future audits.
By embracing these tips, businesses can navigate the complexities of auditing and assurance services more effectively, leveraging the process to drive continuous improvement, strengthen internal controls, and enhance their overall financial and operational performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between auditing and assurance services?
While auditing is a subset of assurance services, the key difference lies in the scope. Auditing focuses specifically on financial statements, verifying their accuracy, completeness, and compliance with relevant standards. Assurance services, on the other hand, are broader, encompassing a wider range of assurance engagements, including internal control audits, operational audits, and attestations on specific business processes.
Why are auditing and assurance services important for businesses?
Auditing and assurance services are essential for businesses as they provide an independent and credible assessment of their financial health, internal controls, and operational processes. This assurance is crucial for building trust among stakeholders, attracting investors, securing financing, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
What are some of the common audit procedures?
Auditors employ a variety of procedures to gather evidence and assess the fairness of financial statements. These include:
- Inspection: Examining documents, records, and tangible assets to verify their existence and accuracy.
- Observation: Observing business processes and activities to assess their effectiveness and compliance with established procedures.
- Inquiry: Seeking information from management and other personnel to obtain relevant details about the business.
- Confirmation: Seeking independent confirmation of information from third parties, such as customers, suppliers, or banks.
- Analytical Procedures: Analyzing financial data to identify unusual or unexpected trends or patterns that warrant further investigation.
How can I find a qualified auditor?
When selecting an auditor, it’s crucial to choose a qualified and reputable firm. Look for firms that:
- Possess the necessary expertise and experience in your industry.
- Adhere to professional standards and ethical guidelines.
- Have a strong track record of providing reliable and independent assurance services.
- Offer a good understanding of your business operations and financial reporting requirements.
Principles Of Auditing & Other Assurance Services Pdf
Conclusion
Understanding the principles of auditing and other assurance services is essential for navigating the complex world of business. These core principles, including independence, professional skepticism, due professional care, and objectivity, form the bedrock of a robust assurance process. By providing independent scrutiny, enhancing internal controls, and promoting transparency, auditing and assurance services play a vital role in building trust, mitigating risks, and fostering a sustainable business environment. As technology and regulatory landscapes continue to evolve, the field of auditing is likely to undergo further transformation, requiring businesses and professionals to stay informed and adapt to the changing dynamics.
Are you interested in learning more about auditing and assurance services? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!




