Have you ever wondered what fueled the tumultuous French Revolution, the fiery spirit that toppled a monarchy and reshaped Europe? Or have you felt a shiver of intrigue at the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, the brilliant general who rose from humble beginnings to become Emperor of France? Perhaps you’re currently grappling with a history assignment, struggling to decipher the complexities of this pivotal period. Well, fear not, for this article is your ultimate guide to navigating the tumultuous waters of the French Revolution and Napoleon’s reign. We’ll delve into the key events, the influential figures, the crucial ideas, and all those perplexing questions that have been swirling in your mind. Buckle up and let’s embark on a journey through time, uncovering the secrets of this fascinating era!

Image: studylib.net
The French Revolution and Napoleon’s rise represent a turning point in European history. It was a period of dramatic upheaval, characterized by revolutionary fervor, bloody conflicts, and sweeping social changes. It’s not just an academic exercise; it’s a story that continues to resonate deeply in our own world, reminding us of the power of ideas, the fragility of power, and the enduring quest for liberty, equality, and justice. This worksheet answer key is your trusted companion, providing the insights you need to not only ace your assignment but also gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped modern Europe.
The French Revolution: A Storm in the Making
The French Revolution did not erupt out of thin air; it was a culmination of years of simmering discontent and societal pressures. Imagine yourself living in pre-revolutionary France – a society divided into rigid social classes, with the vast majority of the population burdened by poverty, inequality, and a lack of representation. The privileged nobility enjoyed luxurious lifestyles while the commoners toiled in the fields, struggling to make ends meet. A rigid social structure, inadequate economic opportunities, and an oppressive tax system fueled resentment among the commoners.
Then came the dire economic woes of the late 18th century. France was facing crippling debt, exacerbated by lavish royal spending and costly wars. Add to this the echoes of the American Revolution, which ignited the ideals of liberty and self-governance, and you have the perfect storm brewing. The discontent, the economic misery, and the longing for freedom combined to create a combustible atmosphere.
The Storm Breaks: Key Events and Turning Points
The French Revolution, in its explosive intensity, can be overwhelming. But let’s break it down into manageable chunks:
1. The Storming of the Bastille (July 14, 1789): It’s a symbolic moment that ignited the revolution. The Bastille, a prison and symbol of royal tyranny, was stormed by Parisian crowds, signaling the end of the absolutist monarchy.
2. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (August 1789): This is a landmark document, echoing the American Declaration of Independence, and enshrining principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity. It fundamentally changed the relationship between the government and the people.
3. The Reign of Terror (1793-1794): This tumultuous period, driven by radical Jacobins, saw a wave of executions and political repression, as the revolution’s fervor turned brutal. A powerful Committee of Public Safety, led by Maximilien Robespierre, oversaw the trials and executions of those deemed enemies of the revolution.
4. The Rise of Napoleon Bonaparte: A brilliant military leader, Napoleon seized power in a coup in 1799, bringing an end to the chaos of the Revolution. He consolidated power and established the French Empire, ushering in a new era.
Understanding Napoleon: From General to Emperor
Napoleon’s legacy is complex, interwoven with triumphs and tragedies. He was a brilliant military strategist, a charismatic leader, and a ruthless conqueror. He rose from obscurity through his military achievements, conquering much of Europe and establishing an empire that stretched from Italy to Spain.
Here are some key aspects of his reign:
- Napoleonic Code: This legal code standardized and modernized French law, abolishing feudal privileges and establishing equality before the law.
- The Napoleonic Wars: Napoleon’s ambition led to a series of wars that ravaged Europe, leaving a trail of destruction and reshaping the political map.
- The Fall of Napoleon: Despite his early successes, Napoleon’s ambition ultimately led to his downfall. The disastrous Russian campaign and the rise of a coalition of European powers brought his empire crashing down, culminating in his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.
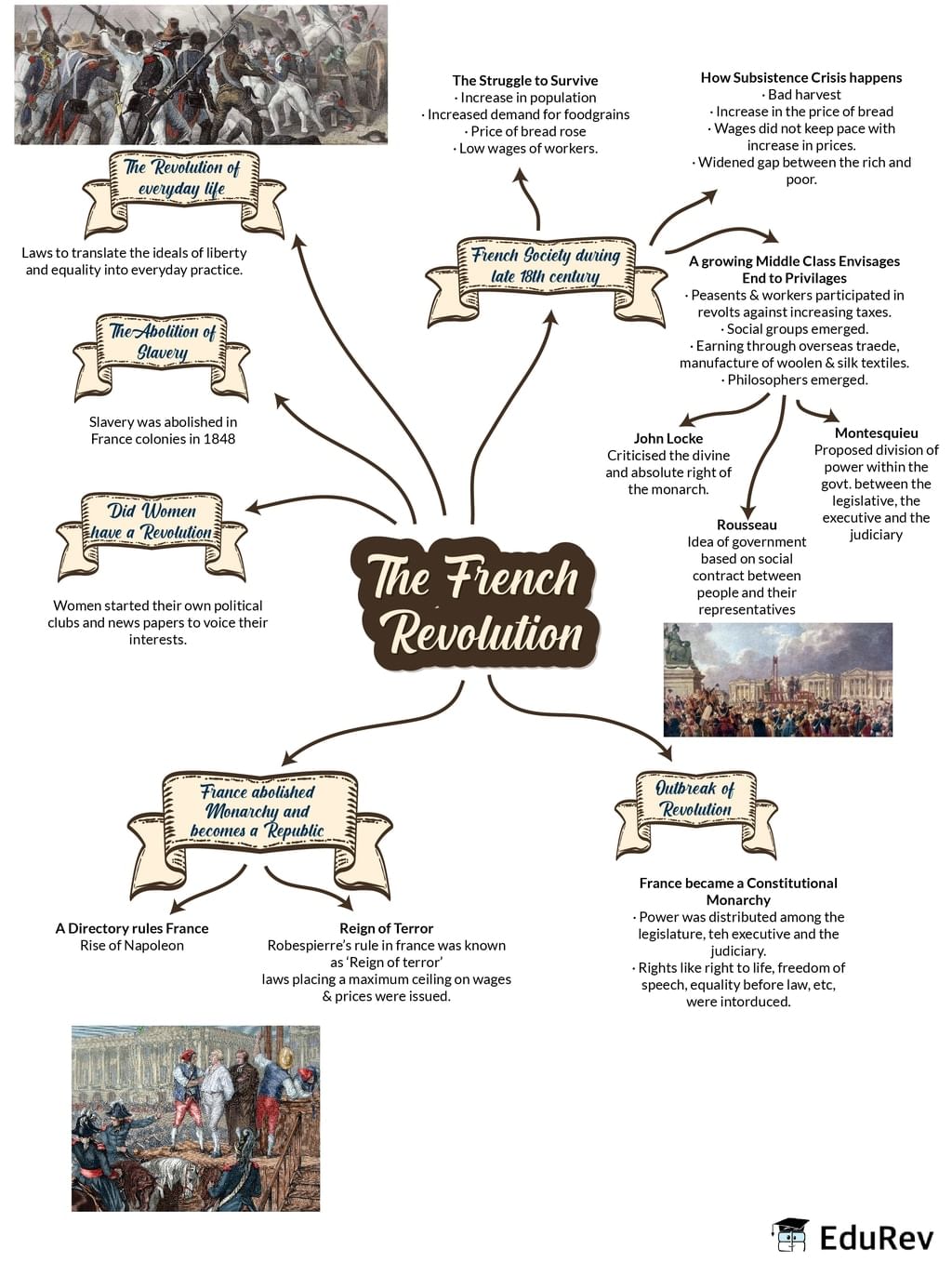
Image: edurev.in
The Enduring Impact
The French Revolution and Napoleon’s reign had a profound impact on Europe and the world. Here are some key takeaways:
- The End of Absolutism: The revolution irrevocably transformed the political landscape of Europe, ushering in the era of representative government and challenging the power of absolute monarchs.
- Rise of Nationalism: Napoleon’s conquests fueled nationalist sentiments across Europe, with people uniting under common identities and rallying against foreign domination.
- The Diffusion of Revolutionary Ideas: The ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity spread across Europe, inspiring future revolutions and shaping the course of history.
The French Revolution And Napoleon Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
Conclusion
The French Revolution and Napoleon’s reign are a testament to the power of ideas, the complexities of political change, and the enduring human quest for freedom. It’s a complex and multifaceted saga woven with intrigue, heroism, and tragedy. As you delve deeper into the details, remember that understanding this era requires empathy, critical thinking, and a willingness to question narratives. Embrace the complexities, challenge assumptions, and explore the echoes of these events in our own time. The world is not static; it is constantly evolving, and its story continues to be written by the enduring forces of change, just as it was during the time of the French Revolution and Napoleon.




