Have you ever received a cryptic message on your car’s dashboard, a string of letters and numbers that seems like a foreign language? This is a common experience for car owners, and chances are you’ve encountered a fault code. These codes are meant to provide valuable insight into what’s going wrong under the hood, but deciphering them can feel like a puzzle. One term that often crops up is “FMI,” standing for “Failure Mode Identifier,” and it plays a crucial role in understanding the nature of the fault.

Image: www.scribd.com
Understanding what FMI means in a fault code is a crucial skill for anyone who wants to take control of their car’s maintenance. By grasping the terminology used in diagnostics, you can collaborate more effectively with mechanics and potentially save money on repair costs. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of fault codes, explore the significance of FMI, and equip you with the knowledge to navigate these digital messages with confidence.
Fault Codes: The Language of Your Car
Fault codes are like cryptic messages from your car, conveying information about potential issues in its complex systems. They are generated by various electronic control units (ECUs) within your vehicle that continuously monitor different aspects, from engine performance to transmission operation. When these ECUs detect an abnormality outside the acceptable range, they record this deviation as a fault code.
Decoding the Code: A Deeper Dive
A typical fault code consists of two main parts:
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC): This part acts like a unique identifier, pinpointing the specific component or system where the problem lies. Think of it as the “address” of the issue.
- Failure Mode Identifier (FMI): This part provides detailed information about the type of malfunction, helping to understand the extent and nature of the problem. Imagine it like the “description” accompanying the address.
FMI: A Closer Look at the Detail
The FMI plays a pivotal role in tailoring the diagnostic process. It acts as a critical bridge between the generic DTC and the specific problem that triggers the code. By understanding the FMI, you can gain valuable insight into what’s causing the issue, potentially leading to faster and more efficient repairs. Here’s what to remember about FMI:
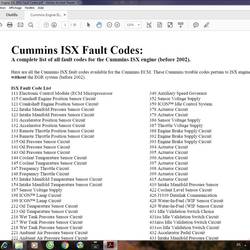
Image: thecampingadvisor.com
FMI Classification: Understanding the Range
FMIs are usually classified on a scale of 1 to 255, although the specific range and interpretation can vary slightly based on the vehicle manufacturer and the type of ECU generating the code. Here are some general categories of FMIs:
- Sensor Issues: Codes with FMIs in this range often indicate problems with sensors, such as oxygen sensors, temperature sensors, or pressure sensors.
- Actuator Problems: These FMIs might suggest malfunctions with actuators like solenoids, valves, or motors responsible for controlling specific functions.
- Circuit Malfunctions: Codes in this category signal issues within the electrical wiring related to the component or sensor in question.
FMI Examples: Bringing It to Life
Let’s consider a few real-world examples to illustrate the importance of FMI:
- DTC: P0171 (System Too Lean) – FMI 1: This code suggests a lean condition in the engine, potentially due to a faulty oxygen sensor. The FMI 1 indicates that the sensor is reporting a consistently lean mixture, potentially leading to performance issues.
- DTC: P0700 (Transmission Control System Malfunction) – FMI 5: This code highlights a problem with the transmission control system. The FMI 5 indicates an internal fault within the control module, potentially leading to transmission shifting issues or complete failure.
How to Use FMIs to Your Advantage
Now that you have a better understanding of what FMI means, let’s explore how you can leverage this information to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s health:
1. Communicating with Your Mechanic
When you bring your car to a mechanic, provide the complete fault code, including the DTC and FMI. This information will help your mechanic quickly pinpoint the problem and potentially save you money on unnecessary diagnostics.
2. DIY Troubleshooting: Using Online Resources
Websites dedicated to automotive diagnostics often provide detailed explanations of fault codes and their associated FMIs. These resources can serve as starting points for your DIY troubleshooting endeavors, empowering you to narrow down potential issues.
3. Avoiding Misinterpretation
While understanding FMIs can be a valuable skill, it’s important to avoid blindly interpreting codes without proper context. Always consult a trusted mechanic or reliable online resources, as misinterpretation can lead to incorrect diagnoses and costly repairs.
What Does Fmi Mean In Fault Code
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital Language of Your Car
The world of fault codes might seem daunting at first glance, but understanding the meaning of FMI empowers you to approach vehicle diagnostics with more clarity and confidence. By recognizing the significance of this detail, you can communicate more effectively with your mechanic and potentially diagnose problems faster, leading to more efficient repairs and greater control over your car’s maintenance. Remember, as you explore further resources, you’ll find this knowledge can become a valuable asset for navigating the “digital language” of your car and ensuring its optimal performance.




