In a world increasingly reliant on digital data, the importance of robust security protocols cannot be overstated. Imagine a bustling online marketplace, transactions flowing seamlessly. Suddenly, chaos erupts, and the platform crashes, leaving users in the dark. A breach? A mistake? Without proper logging and security controls, pinpointing the source of the problem becomes a daunting task. This, unfortunately, is a scenario that plays out too often. Effective security controls on log data are crucial for businesses of all sizes to ensure resilience against cyber threats and maintain trust with customers.
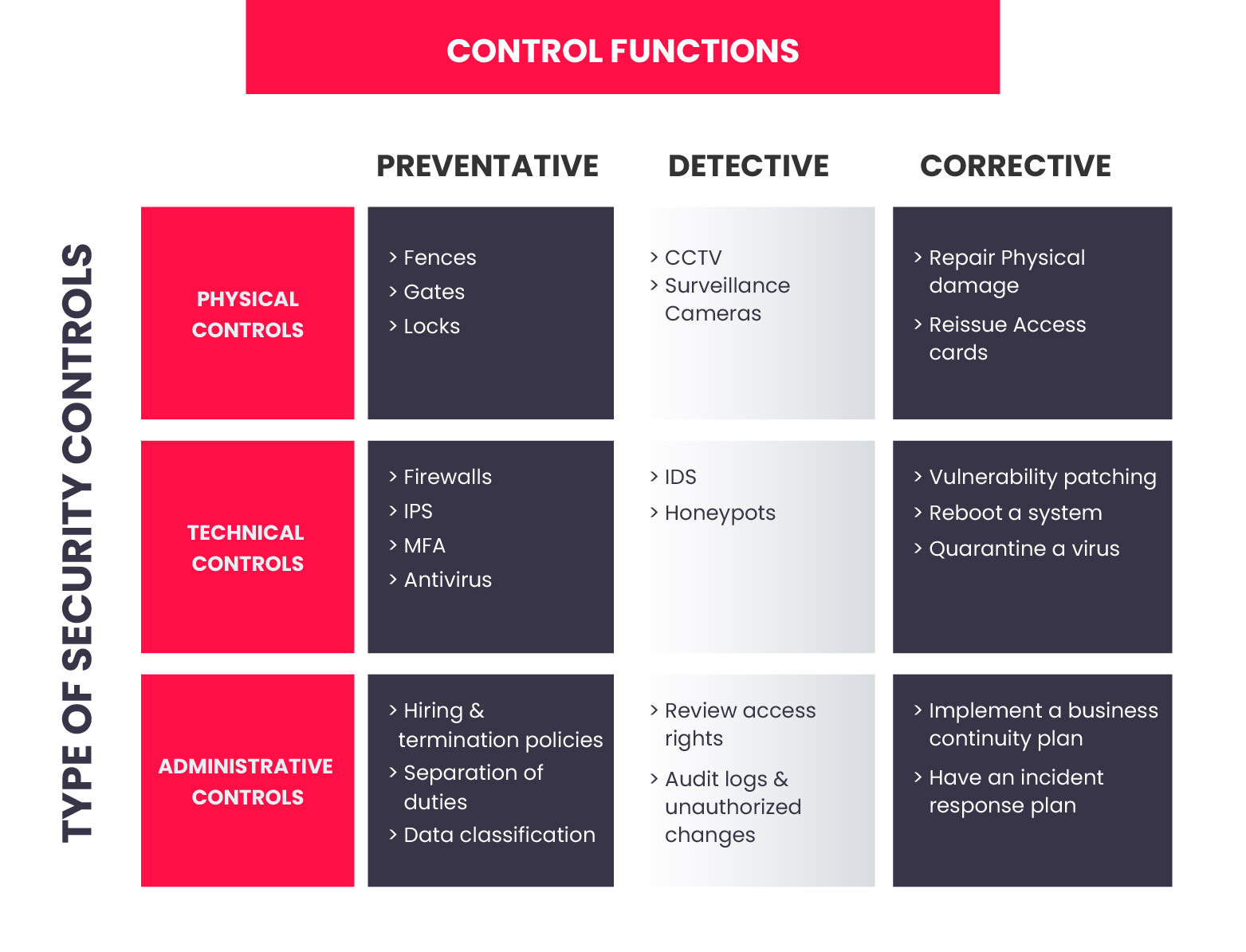
Image: www.infosectrain.com
This article will explore the multifaceted world of log data security controls, highlighting how they should reflect your unique risk posture. We’ll dive into the importance of comprehensive logging, explain different security measures, and emphasize the need for a proactive approach to safeguarding your valuable data.
Understanding the Importance of Log Data Security Controls
Log data, the record of events occurring within your systems, can be a goldmine for security professionals. It allows us to track user activity, detect anomalies, and investigate security incidents. However, the very nature of this data makes it a prime target for attackers as well. Without proper security measures, even the most detailed log data can be compromised or even destroyed.
Consider the analogy of a security camera: It captures footage of your surroundings, but without a secure storage solution, that footage is vulnerable to theft or tampering. Log data security controls act as the “safe” for your digital activity, protecting it from malicious actors and ensuring its integrity.
The Importance of Comprehensive Logging
The first step towards securing log data is ensuring comprehensive logging. This means capturing sufficient details about all relevant events within your systems. Imagine trying to investigate a fire without a detailed fire report: impossible! Similarly, inadequate logging makes security analysis a frustrating and potentially futile exercise. Key areas to focus on include:
- User Activity: Track login attempts, access permissions, and user actions to identify potential insider threats.
- System Events: Record system configuration changes, software updates, and hardware failures for greater visibility into any abnormal changes.
- Network Activity: Capture network connections, traffic patterns, and communication logs to detect malicious network traffic.
- Security Events: Log security alerts, intrusion attempts, and suspicious activity for immediate investigation.
Understanding Your Risk Posture
Before implementing specific security controls, it’s crucial to understand your risk posture. Factors to consider include:
- Industry: Industries like finance and healthcare are prime targets for cyberattacks due to the sensitive nature of their data.
- Data Sensitivity: The more sensitive your data, the higher the need for robust security measures.
- System Complexity: Complex systems with multiple interconnected components require more detailed monitoring and analysis.
- Attack Surface: The more exposed your systems are to the internet, the greater the risk of attack.
By determining your risk level, you can select appropriate security controls that offer the right level of protection.
Image: www.manageengine.com
Security Controls: A Comprehensive Approach
Having comprehensive logging is only half the battle. To safeguard your log data, you need a combination of security measures, each playing a crucial role in the defense strategy.
1. Access Controls and Authentication
Restricting access to log data is essential. Implement strong authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized personnel can view or modify log records. This prevents unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grant access based on user roles, ensuring that each user can only view or modify the data they need.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require users to provide multiple authentication factors (e.g., password and a one-time code) to verify their identity.
2. Encryption
Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, preventing unauthorized access even if the data is intercepted. Encryption is vital for protecting log data both in transit and at rest.
- Data in Transit: Use HTTPS for secure communication between systems, ensuring that log data is protected during transmission.
- Data at Rest: Encrypt log data stored on hard drives, cloud servers, or other storage devices.
3. Integrity Controls
Integrity controls ensure that log data remains unchanged and hasn’t been tampered with. This is crucial for trust in your audit trails and investigations.
- Digital Signatures: Use digital signatures to verify the authenticity and integrity of log files, preventing unauthorized modifications.
- Hashing Algorithms: Generate unique checksums (hashes) for log files, allowing you to detect if any data has been altered.
4. Logging Security and Monitoring
It’s not enough to merely collect log data; you need to monitor it for suspicious activity. Implement security monitoring tools to analyze log data in real-time for anomalies and potential threats.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Centralize log data from multiple sources, correlate events, and generate alerts for suspicious activity.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Integrate threat intelligence feeds into your security tools to detect known malicious patterns and indicators of compromise.
5. Regular Security Audits
To maintain a strong security posture, regular security audits are essential. These audits assess your existing security controls, identify vulnerabilities, and recommend improvements.
- Internal Audits: Conduct internal audits to review your current security practices and ensure they are effective.
- External Penetration Testing: Engage external security experts to simulate attacks and evaluate your security defenses.
Tips and Expert Advice for Securing Log Data
Implementing robust security controls for log data can seem daunting, but by applying strategic principles and proven practices, you can create a secure environment for your vital data.
Here are some expert tips to get you started:
- Prioritize Data Retention: Determine the appropriate retention period for your log data based on regulatory requirements and your organization’s needs. Retain logs long enough to support security investigations and compliance audits.
- Separate Logging from Production: Store log data on separate systems to reduce the risk of attackers compromising log data or using it to gain access to production systems.
- Implement a Vulnerability Management Program: Regularly scan for and patch vulnerabilities in your logging systems and supporting infrastructure.
- Invest in Training: Educate your team about the importance of log data security and provide training on best practices for secure handling and analysis.
- Stay Up-to-Date: Keep abreast of the latest cybersecurity threats and trends and adapt your security controls to address evolving threats.
FAQ about Log Data Security Controls
Here are some frequently asked questions about log data security controls:
Q: What are some common log data security threats?
A: Common threats include unauthorized access, data manipulation, data deletion, denial-of-service attacks, and insider threats.
Q: How can I ensure my log data is not altered or corrupted?
A: Implement integrity controls such as digital signatures, hashing algorithms, and audit trails to detect any changes or tampering.
Q: How do I know if my log data is secure?
A: Conduct regular security audits, use vulnerability scanning tools, and monitor your log data for suspicious activity.
Q: What is the best practice for storing log data?
A: Store log data in a secure location, separate from production systems. Use encryption to protect data both in transit and at rest. Consider using a dedicated log management platform for efficient storage and analysis.
Security Controls On Log Data Should Reflect
Conclusion
Security controls on log data are vital for maintaining data integrity, ensuring compliance, and mitigating security risks. These controls should reflect your specific risk posture, taking into account industry, data sensitivity, and system complexity. By implementing a comprehensive approach that includes access controls, encryption, integrity checks, security monitoring, and regular audits, you can create a secure environment for your valuable log data.
Are you interested in learning more about specific security controls or best practices for managing log data? Share your questions and thoughts in the comments below!




