Imagine a classic, leather-bound encyclopedia resting peacefully on a library shelf. Now imagine a sudden, unexpected gust of wind sweeping through the room, gently pushing the encyclopedia forward. This seemingly innocuous act, a mere nudge, is a perfect example of a net force in action. This force, measured in Newtons (N), is the overall effect of all the forces acting on an object. In this case, the wind’s push is the net force, dictating the encyclopedia’s motion.
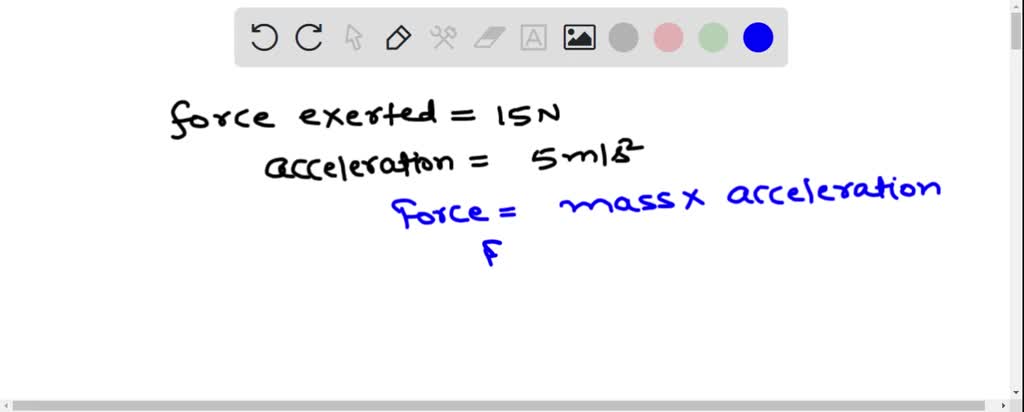
Image: www.numerade.com
While the scenario might sound simple, it highlights a fundamental concept in physics – the direct relationship between forces and motion. Understanding how forces influence an object’s movement, whether it’s an encyclopedia or a rocket ship, is crucial for grasping the world around us. This article delves into the intriguing world of net forces, exploring the impact of applying a 15N net force upon our beloved encyclopedia.
Net Force: The Driving Factor
A net force represents the sum of all forces acting on an object. If multiple forces are acting on an object, we need to consider their direction and magnitude to determine the net force. If forces are acting in the same direction, they are added together. If they act in opposite directions, they are subtracted. Imagine pushing a heavy box across a room. You’re applying a force to move the box forward, but friction between the box and the floor opposes your effort. The difference between these two forces is the net force, dictating how quickly and in what direction the box moves.
In the case of our encyclopedia, a 15N net force implies that the combined effect of all forces acting on it results in a 15 Newton push. This can be caused by a single force, like a strong wind, or a combination of forces, such as a gentle push from someone combined with a slight breeze.
Newton’s Laws: The Foundation of Motion
To understand how a 15N net force affects our encyclopedia, we need to turn to Sir Isaac Newton’s groundbreaking laws of motion. These laws form the bedrock of classical mechanics and are essential for comprehending the movement of objects in our everyday world.
Newton’s First Law: The Law of Inertia
Newton’s first law, often dubbed the “law of inertia,” explains that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant speed and direction unless acted upon by an external force. This means our encyclopedia will remain stationary on the shelf until an external force disrupts its state of rest. The 15N net force acts as that external factor, causing the encyclopedia to move.

Image: brainly.com
Newton’s Second Law: F = ma
Newton’s second law of motion is the heart of the matter. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. In simpler terms, the greater the net force, the greater the acceleration. This means a 15N net force applied to our encyclopedia will cause it to accelerate at a specific rate, depending on its mass.
Newton’s Third Law: Action and Reaction
Newton’s third law introduces the concept of pairs of forces. This law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When the 15N net force acts on our encyclopedia and sets it in motion, an equal and opposite reaction force is exerted back on the source of that force. This is why you might feel a push back when you push against a wall.
Applying a 15N Net Force to an Encyclopedia
Now, let’s examine the practical implications of a 15N net force applied to our encyclopedia. First, we need to consider the encyclopedia’s mass. This is crucial because, as Newton’s second law reveals, the mass directly impacts the acceleration resulting from the net force.
Let’s assume our encyclopedia has a mass of 5 kg. Using Newton’s second law, we can calculate the resulting acceleration:
a = F/m
a = 15N / 5 kg
a = 3 m/s²
This means that the encyclopedia will accelerate at a rate of 3 meters per second squared.
The impact of this force will be dependent on the encyclopedia’s initial state. If it was initially at rest, the 15N net force will cause it to start moving, gaining speed at the calculated acceleration rate. However, if it was already moving, the force will either increase its speed, change its direction, or both. In a real-world scenario, the 15N net force would not act for an indefinite period. Air resistance, friction with the shelf, and other forces would come into play, eventually slowing the encyclopedia down until it settles back to rest.
Exploring the Forces: Beyond the Basics
In real-world scenarios, the force acting on an encyclopedia might not be a constant 15N. It could be variable, oscillating, or depending on other factors. We may also need to consider forces like friction, air resistance, and even the shape and structure of the encyclopedia itself for a more comprehensive prediction of its motion.
The application of these concepts extends far beyond the humble encyclopedia. Engineers utilize these principles to design everything from aircraft to bridges, ensuring they can withstand various forces and remain stable. Physicists use these fundamental laws to analyze the behavior of galaxies, understand the formation of stars, and explore the depths of our universe.
Expert Advice: Understanding Forces in Everyday Life
If you’re interested in learning more about forces, the first step is to observe the world around you. Pay attention to how objects move and interact. Whenever you see an object at rest or in motion, think about what forces are acting on it and how they affect its behavior.
You can also delve deeper into the study of physics, examining topics such as work, energy, and momentum. These concepts are closely related to forces and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the physical world. Try reading books or watching videos that explain physics concepts in simple terms. You can even conduct simple experiments at home, such as rolling balls down ramps or swinging pendulums, to observe forces in action.
FAQ: Common Questions about Net Force
Q: What is the difference between force and net force?
Force is a push or pull acting on an object, while net force is the sum of all forces acting on an object. If multiple forces are acting on an object, the net force determines the object’s overall motion.
Q: If a net force of 15N is applied to a heavier encyclopedia, will the acceleration be the same?
No, the acceleration will be lower. Newton’s second law tells us that the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass. A heavier encyclopedia will experience less acceleration with the same net force.
Q: Can a net force of 15N cause an encyclopedia to move sideways?
Absolutely! The direction of the net force dictates the direction of the object’s motion. If the 15N force is applied sideways, the encyclopedia will move sideways.
Q: Is it possible for an object to have no net force acting on it?
Yes, if multiple forces are acting on the object and they perfectly balance each other, the net force is zero. This is why an object at rest remains at rest, as the forces on it, like gravity, and the support force from the surface it’s on, are balanced.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Forces
By examining the effects of a 15N net force on an encyclopedia, we’ve delved into fundamental principles of physics, discovering how forces govern the motion of objects in our world. From Newton’s Laws to the real-world implications of net forces, this journey highlights the crucial role physics plays in understanding our environment. So next time you see an encyclopedia resting on a shelf, remember the unseen forces that keep it in place and the potential for motion that lies within every object we encounter.
A Net Force Of 15n Is Exerted On An Encyclopedia
Are you fascinated by the world of forces and motion? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!




