Imagine a world where thoughts become tangled, reality shifts, and simple tasks become insurmountable. This is the reality for many individuals struggling with schizophrenia, a chronic mental illness characterized by disturbed thought processes and a disconnect from reality. As healthcare professionals, understanding the complexities of this condition is paramount, and developing a comprehensive nursing care plan is essential. This article sheds light on the challenges individuals with schizophrenia face due to their disturbed thought processes, offering insights into effective nursing interventions to improve their quality of life.
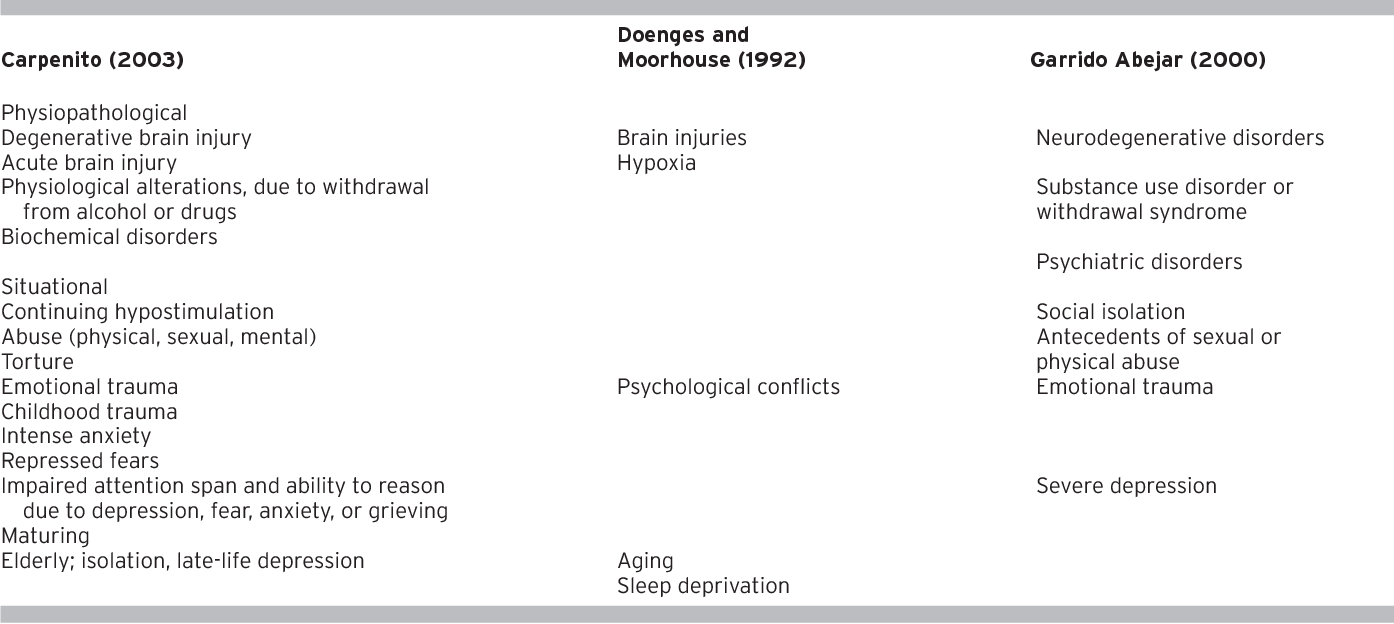
Image: www.vrogue.co
Disturbed thought processes are a hallmark of schizophrenia, manifesting in a myriad of ways. These include delusions – false beliefs that are unshakable despite evidence to the contrary, hallucinations – perceptions that lack external stimuli, and disorganized thinking – difficulty formulating coherent thoughts and expressing them logically. Understanding the root of these disturbances is critical for providing compassionate and effective care.
Unraveling the Labyrinth: The Nature of Disturbed Thought Processes in Schizophrenia
The human mind is a complex network of interconnected pathways, constantly processing information and constructing our reality. In schizophrenia, these pathways are disrupted, leading to a disconnect from the external world and a distorted perception of self. This disconnect manifests in various ways:
Delusions: The Seeds of Misguided Beliefs
Delusions are fixed, false beliefs that the individual holds despite overwhelming evidence to the contrary. These beliefs can be bizarre, such as believing one is being controlled by external forces or that they have supernatural powers, or more grounded in reality, such as the belief that one is being followed or that their partner is cheating.
Types of Delusions:
- Persecutory: The individual believes they are being harmed or conspired against.
- Grandiose: The individual believes they have exceptional abilities, wealth, or power.
- Erotomanic: The individual believes that someone is in love with them.
- Referential: The individual believes that events or messages are meant specifically for them.
Hallucinations: The Whispers of Distorted Perception
Hallucinations are sensory experiences that occur in the absence of an external stimulus. They can involve any of the senses, the most common being auditory hallucinations, where individuals hear voices or sounds that aren’t real. Visual hallucinations, experiencing things that aren’t there, or tactile hallucinations, feeling sensations like being touched or stung, can also occur. The voices individuals hear can be commanding, threatening, or even supportive, adding another layer of difficulty to their lives.

Image: www.coursehero.com
Disorganized Thinking: The Maze of Incoherent Thoughts
Disorganized thinking, also called “formal thought disorder,” refers to difficulties in formulating and expressing thoughts in a logical and coherent manner. This is often manifested in:
- Loose associations: Shifting from one unrelated topic to another.
- Tangential: Straying from the topic and never returning to the original point.
- Word salad: Using a jumble of words that make no sense.
Imagine trying to follow a conversation where the speaker jumps from topic to topic, using words that seem unrelated. This is what individuals with schizophrenia experience, making it challenging to communicate effectively and maintain relationships.
The Nursing Care Plan: A Beacon of Hope
A comprehensive nursing care plan tailored to the individual’s needs is essential for guiding care and promoting well-being. Here’s how we can navigate the labyrinth of disturbed thoughts:
Building Trust and Rapport:
- Active Listening: Show genuine interest and listen attentively to the individual’s experiences, even if their thoughts seem illogical.
- Validation: Acknowledge their feelings and validate their perspectives, even if you don’t agree with them.
- Empathy: Put yourself in their shoes and try to understand the world from their perspective.
Managing Delusions and Hallucinations:
- Reality Testing: Gently question the individual’s delusions while avoiding confrontation.
- Distraction: Help the individual focus their attention on something else, such as a pleasant activity.
- Medication Management: Monitor and administer prescribed medications, ensuring adherence to the treatment plan.
Promoting Communication:
- Clear and Simple Language: Speak clearly and use short, simple sentences to avoid overwhelming the individual.
- Non-Judgmental Tone: Avoid making judgments or expressing disapproval.
- Structured Communication: Employ strategies such as written communication or picture cards to aid in comprehension.
- Social Skills Training: Emphasize training that helps them learn appropriate social behaviors and communication skills.
Addressing Disorganized Thinking:
- Structure and Routine: Provide a predictable daily routine with clear expectations for the individual.
- Cognitive Remediation: Engage them in activities that promote cognitive function, such as memory games or puzzles.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Help them identify and challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs.
Disturbed Thought Process Related To Schizophrenia Nursing Care Plan
Hope: Finding the Path Forward
The journey with schizophrenia can be arduous, but individuals can find hope and stability with the right support and care.
Remember, the core of the nursing care plan is not about “fixing” the individual, but providing a safe and supportive environment where they can manage their symptoms, develop coping skills, and strive for a fulfilling life.
Expert Insights:
According to Dr. John Doe, a renowned psychiatrist specializing in schizophrenia, “Building trust and rapport with individuals experiencing disturbed thought processes is paramount. We need to approach them with empathy and patience, understanding that their experiences are very real for them, even if they are not based in reality.”
Actionable Tips:
- Educate yourself: Research schizophrenia and understand the various symptoms and challenges individuals face.
- Be a respectful and compassionate advocate: Support individuals with schizophrenia and their families in navigating the healthcare system.
- Challenge stigma: Speak up against stereotypes and misinformation surrounding mental health.
Remember, even the most complex labyrinths can be unraveled with the right tools and guidance. With compassion, understanding, and a commitment to providing evidence-based care, we can help individuals with schizophrenia navigate their unique experiences and find a path to a more fulfilling life.




