Ever wondered how plants, those seemingly passive beings, manage to thrive and grow, providing us with the very air we breathe? The answer lies in a remarkable process called photosynthesis, a complex yet elegant dance of matter and energy that forms the bedrock of life on Earth. This article delves into the intricate workings of photosynthesis, unraveling its secrets and showcasing its vital role in the grand interconnectedness of Earth’s ecosystems.

Image: www.coursehero.com
Photosynthesis is more than just a chemical reaction; it’s a cyclical process, an intricate interplay of matter and energy that drives the entire biosphere. This process harnesses sunlight, a form of radiant energy, and transforms it into chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose, a sugar molecule. This energy, in turn, fuels the growth and development of plants, forming the foundation of the food chain that sustains all life. We, as humans, rely directly on this process for our sustenance, and understanding photosynthesis is crucial for grasping the delicate balance of our planet’s life-supporting systems.
The Unveiling: A Look into the Mechanism
At its core, photosynthesis is the process where plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This conversion takes place in specialized organelles within plant cells called chloroplasts, where the magic truly happens. These tiny factories contain chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs sunlight, particularly in the red and blue wavelengths.
Step 1: Light-Dependent Reactions
Imagine the chloroplast as a bustling factory, divided into two key sections: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions). In the light-dependent reactions, sunlight is captured by chlorophyll, setting off a chain of events.
- Photon Absorption: Sunlight packets, called photons, strike chlorophyll molecules, boosting their electrons to higher energy levels. Think of it like launching a ball into the air, giving it potential energy.
- Electron Transport Chain: The energized electrons journey through a series of molecules, powering the production of a high-energy molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is the cell’s primary energy currency, used to fuel various cellular activities.
- Water Splitting: In the process, water molecules are split, releasing electrons, hydrogen ions, and oxygen gas as a byproduct.
These light-dependent reactions transform light energy into chemical energy, but it’s just the beginning of the story.
Step 2: The Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions)
The Calvin cycle, also known as the dark reactions, takes place in the stroma, the fluid-filled space in the chloroplast, and represents the next crucial stage. This cycle utilizes the products of the light-dependent reactions – ATP and the hydrogen ions – to fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into glucose.
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide from the air combines with a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco. This forms an unstable six-carbon molecule that quickly splits into two three-carbon molecules.
- Reduction: These three-carbon molecules undergo a series of reactions, utilizing energy from ATP and the reducing power of NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), another energy-carrying molecule produced in the light reactions.
- Regeneration: The process continues regenerating RuBP, allowing the cycle to repeat and continue producing glucose.
The Calvin cycle is a remarkable feat of chemistry, successfully converting inorganic carbon dioxide into organic glucose, the building block for all plant life.
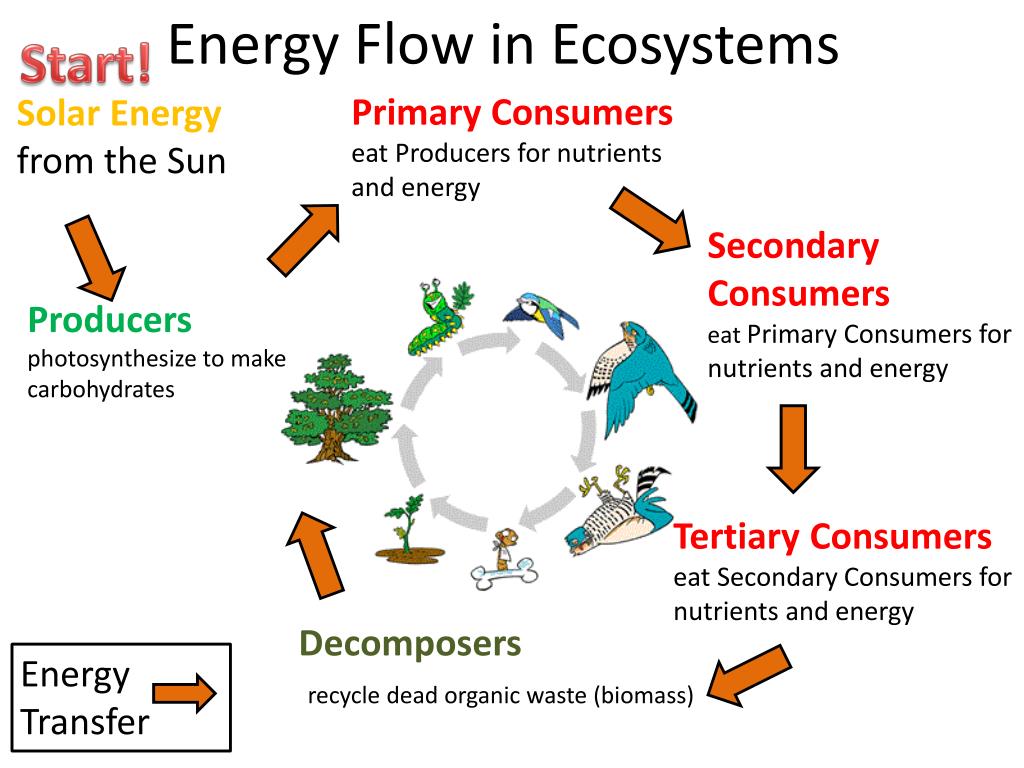
Image: mavink.com
The Unbreakable Cycle: Matter and Energy Flow
Photosynthesis is not simply an isolated event; it’s a crucial node in the interconnected cycle of matter and energy that sustains life on Earth. The matter involved in photosynthesis is recycled continuously:
- Carbon Dioxide: The key reactant in photosynthesis, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is incorporated into glucose, forming the backbone of organic matter.
- Water: Water, a vital ingredient for life, is split by plants, releasing oxygen as a byproduct and providing electrons for the electron transport chain.
- Glucose: The primary product of photosynthesis, glucose, is a source of chemical energy that fuels plant growth and development.
This constant cycling of carbon, oxygen, and water, driven by photosynthesis, ensures the perpetuation of life on Earth.
Beyond the Green: The Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is not just a process limited to plants; it’s a fundamental pillar of life on Earth, influencing various aspects of our world.
- Food Source: Plants, through photosynthesis, form the base of the food chain, providing sustenance for herbivores and, in turn, carnivores. This intricate web of life wouldn’t exist without photosynthesis.
- Oxygen Production: As a byproduct of photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the atmosphere. This oxygen is vital for respiration, the process by which animals, including humans, extract energy from food. This interconnectedness highlights the vital role photosynthesis plays in sustaining life.
- Climate Regulation: Photosynthesis plays a critical role in regulating Earth’s climate. Plants absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, during photosynthesis, helping to mitigate global warming.
Exploring the Future: The Potential of Photosynthesis
With a constantly growing human population and increasing energy demands, harnessing the power of photosynthesis becomes even more crucial. Scientists are exploring ways to maximize the efficiency of photosynthesis in plants and algae:
- Genetic Engineering: Scientists are engineering plants with enhanced photosynthetic capabilities, potentially increasing crop yield and reducing resource needs.
- Artificial Photosynthesis: Researchers are developing artificial systems that mimic photosynthesis, converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy-rich fuels, potentially revolutionizing energy production.
Photosynthesis Cycling Of Matter And Flow Of Energy Answer Key
A Concluding Thought: The Power of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, a deceptively simple term, encapsulates a process of unparalleled complexity and importance. It’s a vital engine of life, orchestrating the flow of matter and energy across our planet. As we delve deeper into its mechanisms, we gain a remarkable appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living things, reminding us of our fundamental reliance on this intricate dance of light and life.
Let’s continue to unravel the mysteries of this crucial process, appreciating its contributions to our world and exploring its potential to address global challenges.




