Have you ever found yourself scratching your head, wondering what a Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number is and why it’s so important? As a business owner handling transactions, I know the frustration of navigating the complex world of payment processing. You may have encountered situations where a crucial detail, like the routing number, was missing, creating delays or even jeopardizing your transactions. This guide will demystify the role of Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers and offer a comprehensive understanding of their significance in the financial ecosystem.
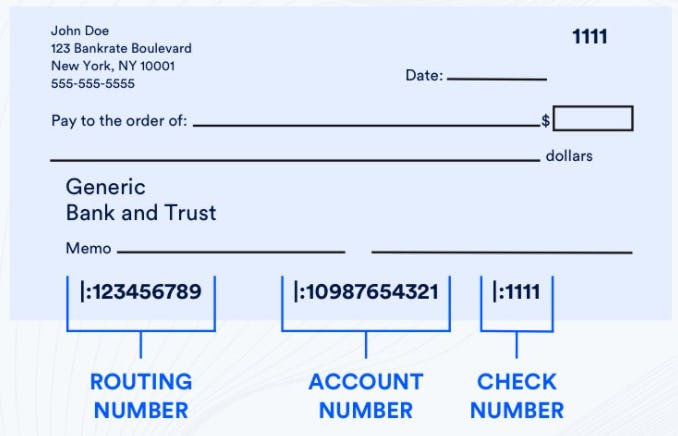
Image: statrys.com
This article will delve into the specifics of Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers, exploring their purpose, structure, and application in different financial scenarios. We’ll navigate through the intricacies of this crucial data point, answering your questions and equipping you with the knowledge to confidently handle your financial transactions.
Understanding Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers
At its core, the Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number, also known as the ABA Routing Number or simply Routing Number, is a nine-digit code used by banks and financial institutions to identify specific branches within the Federal Reserve System. The Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States, operates as a network connecting various financial institutions across the country. Every branch of the Federal Reserve is assigned a unique routing number, facilitating seamless financial transactions among participating banks.
What is the Purpose of a Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number?
Imagine a complex network of pipes carrying water throughout a vast city. These pipes represent the various financial institutions, and the water flowing through them symbolizes financial transactions. The Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number serves as the address for each pipe, guiding the flow of money within the network. Essentially, this number ensures that funds are directed to the correct financial institution or branch, ensuring the smooth processing of transfers, payments, and other financial transactions.
The Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number acts as a critical identification tool, distinguishing one bank or branch from another. It assists in identifying the exact location where a specific account is held within the Federal Reserve System. When you initiate a transfer or make a payment, the routing number acts as a map, guiding the transaction to the correct destination. The accurate use of routing numbers is pivotal in preventing funds from being mistakenly directed to the wrong location, ensuring efficient and secure money movement.
How are Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers Structured?
The Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number is composed of nine digits, each holding specific meaning. Let’s break down its structure:
- Digits 1-4: Identify the specific Federal Reserve Bank District or branch responsible for processing the transaction.
- Digits 5-8: Represent the specific bank or financial institution within that Federal Reserve District.
- Digit 9: Serves as a “check digit” used to verify the accuracy of the first eight digits. It helps prevent errors during data transmission.
Image: www.pxfuel.com
How to Find Your Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number
Obtaining your bank’s Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number is straightforward. It can be found on various documents and tools:
- Checks: The routing number is typically printed in the bottom-left corner of your checks, alongside your bank account number.
- Bank Statements: Check your bank statements, as they often display the routing number prominently.
- Online Banking: Your online banking portal will usually provide access to your account details, including the routing number.
- Contact Your Bank: If you’re unable to locate your routing number through other means, simply contact your bank’s customer service department, and they will be able to provide it to you.
The Importance of Accuracy
In the realm of financial transactions, accuracy is paramount. The slightest error in a Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number can lead to significant complications, potentially delaying transactions or causing funds to be diverted to the wrong account. It’s essential to double-check the routing number, ensuring that it is correct before initiating any financial transaction.
Inaccurate routing numbers can result in various issues:
- Transaction Delays: When an incorrect routing number is used, the transaction may be flagged as suspicious or invalid, leading to significant delays in processing.
- Failed Transactions: Mistyped routing numbers can result in entirely failed transactions. This is particularly problematic for time-sensitive payments or transfers, such as those associated with bills or deadlines.
- Incorrect Account Transfers: A wrong routing number can cause funds to be credited to the wrong account, creating complications and potential discrepancies in your financial records.
Where are Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers Used?
Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers play a critical role in various financial processes, enabling the smooth flow of funds within the banking system.
- Electronic Funds Transfers (EFTs): EFTs, such as online transfers, direct deposits, and bill payments, rely heavily on routing numbers to ensure accurate routing of funds.
- Wire Transfers: For large transactions requiring swift and secure transfer of funds, routing numbers are essential for directing the money to the correct recipient.
- ACH Transactions: Automated Clearing House (ACH) transactions, which handle recurring payments and payroll, utilize routing numbers to identify the specific bank or account for crediting or debiting funds.
- Check Processing: When you deposit a check, the routing number helps banks identify the institution that issued the check and process the transaction efficiently.
Keeping Up with the Latest Trends in Routing Number Usage
The financial landscape is constantly evolving, with technological advancements transforming how we handle money. While the core purpose of routing numbers remains consistent, there are ongoing developments impacting their usage. The rise of financial technology (FinTech) and digital payments, such as mobile wallets and peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms, has introduced new ways to initiate and receive funds. The Federal Reserve and other financial institutions are adapting to these trends, ensuring secure and efficient transaction processes.
Expert Tips for Dealing with Routing Numbers
Based on my experience in managing financial transactions, here are some essential tips to avoid common routing number pitfalls:
- Double-Check: Always double-check the accuracy of a routing number before initiating any financial transaction. A simple typo can lead to significant delays or complications.
- Verify Sources: Obtain routing numbers only from reliable sources, such as your bank’s website or official documents. Avoid relying on unverified sources or online databases that may not always be up-to-date.
- Keep Records: Maintain clear records of all your routing numbers, especially those related to your business accounts. This allows for easy reference and reduces the risk of errors.
By following these tips and understanding the nuances of routing numbers, you can streamline your financial transactions, minimize potential issues, and ensure that your funds are directed efficiently and securely.
FAQs About Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers
Q: What is the difference between a routing number and an account number?
A routing number identifies the specific bank or branch where your account is located within the Federal Reserve System. In contrast, an account number is unique to your individual account within the specific bank or branch.
Q: Can I use the same routing number for all my accounts at different banks?
No, each bank or branch has its own unique routing number. The routing number will differ for your accounts at different financial institutions. You should use the correct routing number associated with each specific account.
Q: What if I accidentally enter the wrong routing number?
Mistakes happen! If you realize you’ve entered the wrong routing number, contact your bank immediately to report the error. They may be able to rectify the situation, but the process could involve delays and additional steps.
Q: Is there a central database where I can find routing numbers?
While several online databases claim to provide routing numbers, their accuracy and security can be questionable. It’s best to obtain routing numbers directly from your bank or official sources.
Q: Are Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers the same for international transactions?
International transactions typically require a different system of identification known as SWIFT codes. The Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number is primarily used within the United States, and a SWIFT code is necessary for international transfers.
Federal Reserve Bank Routing Number List
Conclusion
Understanding the workings of Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers is crucial for navigating financial transactions smoothly. These nine-digit codes serve as the backbone of our financial system, ensuring that funds are accurately routed to the correct destination. By using them correctly, you can ensure your transactions are processed efficiently, minimizing delays and safeguarding your funds.
Are you still confused about Federal Reserve Bank Routing Numbers, or do you have any additional questions? Let us know in the comments section below! We’re here to help you navigate the intricacies of the financial world, so don’t hesitate to ask.




