Have you ever been tasked with managing a complex project with numerous tasks and dependencies? Juggling deadlines, allocating resources, and ensuring everything runs smoothly can feel like a balancing act on a tightrope. Imagine trying to launch a new product, where design, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution all need to be coordinated seamlessly. This is where the Critical Path Method (CPM) comes into play. Think of it as a roadmap designed to help you navigate the complexities of project management by identifying the most crucial tasks that directly impact the overall project completion time.

Image: www.xn--kton-7na7896b.vn
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the Critical Path Method, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its principles, steps, and practical applications. We’ll explore a real-world example with a downloadable PDF solution, guiding you through the process of applying CPM to your own projects. Get ready to unlock a valuable tool for optimizing project timelines, minimizing delays, and ensuring successful project completion!
Understanding the Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to determine the shortest possible time to complete a project. It involves identifying and analyzing all the activities that need to be performed, as well as their dependencies, durations, and resources. By mapping these elements, CPM helps identify the critical path – the sequence of tasks that directly affect the project’s completion date.
The critical path represents the longest sequence of tasks, and any delays in these critical activities will directly impact the project completion date. By focusing on these critical tasks, project managers can allocate resources effectively, monitor progress closely, and take proactive measures to mitigate potential delays.
Key Concepts in Critical Path Method
Before we delve into an example, it’s essential to understand the key elements that make up the Critical Path Method:
1. Activities and Tasks
The first step is to break down the project into individual activities or tasks. These tasks represent the smallest units of work that need to be completed.
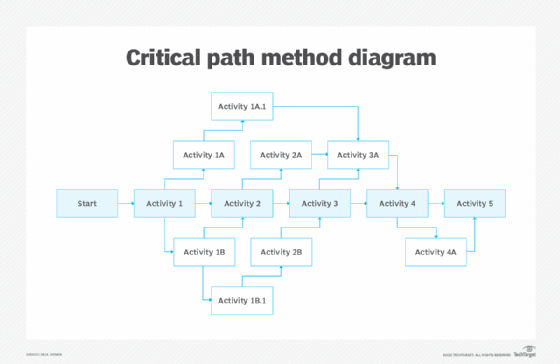
Image: www.techtarget.com
2. Dependencies
Activities within a project are often interconnected. Dependencies indicate that some tasks cannot be started until others are completed. These relationships are crucial for understanding how activities flow within the project.
3. Durations
Each activity needs an estimated duration, which represents the time required to complete that task. Accurate duration estimates are essential for CPM, as they directly influence the project’s overall timeline.
4. Resources
Identifying the resources needed for each task, such as manpower, materials, or equipment, is crucial for effective resource allocation and project management.
5. Critical Path
The critical path is the sequence of activities that have the longest total duration, and any delay in these activities directly impacts the project completion date. It represents the minimum time needed to complete the entire project, considering dependencies among tasks.
6. Slack
Slack refers to the amount of “float” or wiggle room available for non-critical activities. This means that tasks with slack can be delayed without affecting the overall project deadline. Understanding slack enables efficient resource allocation and flexibility in project management.
Critical Path Method Example with Solution PDF
Let’s consider a simple example to illustrate the application of the Critical Path Method. Imagine you’re planning a wedding. The wedding planning process can be broken down into several activities, each requiring time and resources. Here’s a simplified example:
Project: Wedding Planning
Activities in the wedding planning project include:
- Set the Date: 1 week
- Choose Venue: 2 weeks
- Send Invitations: 3 weeks (depends on Venue selection)
- Book Caterer: 2 weeks (depends on Venue selection)
- Select Dress: 2 weeks
- Plan Wedding Ceremony: 3 weeks (depends on Venue selection)
- Arrange Music: 2 weeks (depends on Venue selection)
- Book Photographer and Videographer: 2 weeks
To determine the critical path, we need to consider the dependencies between these tasks. For example, setting the date is crucial before selecting the venue and other activities. Similarly, you cannot book the caterer until the venue is chosen. We can represent these dependencies visually using a network diagram, also known as an Activity-On-Node (AON) diagram.
Network Diagram:
Imagine the AON diagram here depicting the tasks and dependencies described above. For simplicity, let’s assume the following dependencies:
- Activity 1 (Set the Date) occurs before all other activities.
- Activity 2 (Choose Venue) must be completed before activities 3, 4, and 6.
- Activities 3, 4, and 6 must be completed before Activity 8 (Book Photographer and Videographer).
Critical Path Calculation:
By analyzing the dependencies and durations, we can identify the longest sequence of tasks, which will represent the critical path. In this simplified example, the critical path is likely to be:
- Set the Date (1 week)
- Choose Venue (2 weeks)
- Send Invitations (3 weeks)
- Book Photographer and Videographer (2 weeks)
The critical path has a total duration of 8 weeks. This means the wedding cannot take place before 8 weeks have passed. Any delays in any of these critical activities will delay the wedding date.
Tips for Effective Critical Path Method Implementation
Here are some tips for successfully implementing the Critical Path Method in your projects:
- Clearly Define Activities and Tasks: Break down the project into manageable tasks, ensuring each activity is clearly defined and measurable.
- Accurate Duration Estimates: Use historical data, expert opinions, and industry benchmarks to ensure realistic and accurate duration estimates for each activity.
- Identify Dependencies: Pay close attention to the relationships between activities, as dependencies significantly impact project timelines. Clarify and document any precedence or logical relationships.
- Use Scheduling Software: Utilize project management software like Microsoft Project, Primavera P6, or Smartsheet to efficiently create network diagrams, track progress, and manage tasks. These tools automate critical path analysis and provide valuable insights.
- Regular Monitoring and Communication: Monitor the project closely, track progress against the critical path, and communicate changes effectively to all stakeholders. Regular updates and proactive adjustments can mitigate potential delays.
FAQs
Here are some common questions regarding the Critical Path Method:
Q1: What are the benefits of using the Critical Path Method?
The Critical Path Method offers several benefits, including:
- Improved Project Planning: CPM provides a structured framework for planning and managing complex projects.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: By focusing on critical tasks, CPM enables you to allocate resources effectively where they are most needed.
- Reduced Project Delays: CPM identifies potential delays and provides insights for proactive risk mitigation strategies.
- Enhanced Communication: CPM facilitates communication among project stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned on timelines, dependencies, and critical activities.
Q2: Are there any limitations to the Critical Path Method?
While CPM is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations:
- Accuracy of Estimates: The accuracy of the Critical Path Method relies heavily on the accuracy of duration estimates and understanding dependencies. Inaccurate data can lead to unreliable results.
- Complexity: CPM can be complex for large projects with numerous tasks and dependencies, requiring significant time and effort to develop and maintain network diagrams.
- Flexibility: CPM may not be suitable for projects with high levels of uncertainty or dynamic changes in requirements.
Q3: How do I create a PDF solution for my own project using the Critical Path Method?
You can use project management software or tools to create a network diagram and critical path analysis for your project. Once done, you can export the analysis in PDF format. Many tools allow you to customize the appearance of the PDF, including adding logos, formatting, and adding additional information tailored to your needs. Alternatively, you can manually create a network diagram and critical path analysis using a drawing software or spreadsheet software, and then export it as a PDF.
Critical Path Method Example With Solution Pdf
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method is a valuable tool for managing projects effectively by identifying critical tasks, optimizing timelines, and minimizing delays. By understanding the key concepts, applying the steps, and utilizing the tips provided in this article, you can successfully implement CPM for your projects, delivering them on time and within budget. Are you ready to streamline your project planning and achieve greater success?




