Imagine a life where your emotions are like a roller coaster, soaring to manic heights one minute and plummeting into depressive depths the next. This is the reality for individuals living with bipolar disorder, a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings. These swings can profoundly impact their daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. As a nurse, understanding the complexities of this disorder and developing a comprehensive care plan is crucial to help patients navigate these emotional storms and regain control of their lives.

Image: www.coursehero.com
This article delves into the intricacies of bipolar disorder, providing a comprehensive nursing care plan designed to address the unique needs of individuals struggling with this condition. By understanding the different phases of bipolar disorder, the impact on an individual’s life, and the essential nursing interventions, we can empower patients and families with the knowledge and tools to manage the challenges of this complex mental health condition.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition that causes significant shifts in a person’s mood, energy, and ability to think clearly. These shifts are called “mood episodes” and can range from periods of intense highs (mania or hypomania) to extreme lows (depression).
Phases of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is characterized by two distinct phases:
- Manic or hypomanic episodes: These episodes involve a period of elevated mood, increased energy, and racing thoughts. Individuals in a manic state may experience a decreased need for sleep, engage in risky behaviors, and have difficulty concentrating. Hypomania is a less severe form of mania with similar symptoms but less disruptive to daily life.
- Depressive episodes: These episodes are marked by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. Other symptoms may include fatigue, changes in appetite and sleep, and suicidal thoughts.
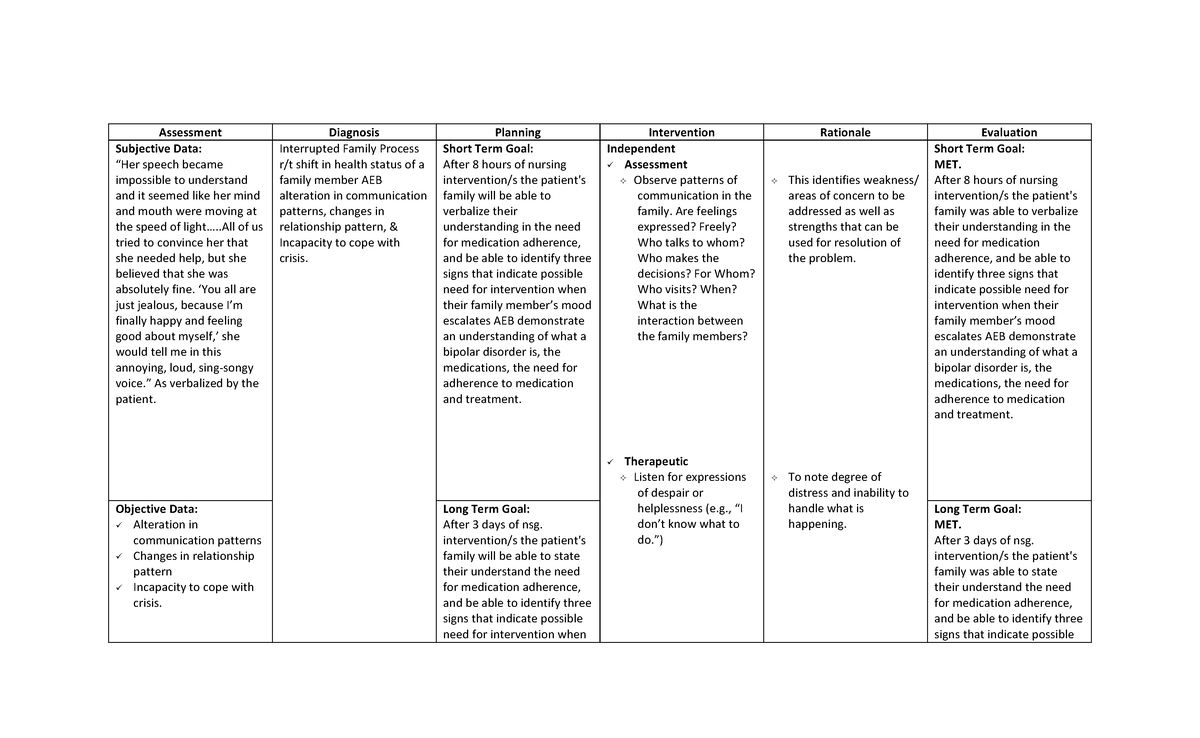
Image: www.studocu.com
Impact of Bipolar Disorder on Daily Life
Bipolar disorder can severely impact various aspects of a person’s life, including:
- Relationships: Mood swings can strain personal and professional relationships, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Work and school: Difficulty concentrating and unpredictable mood changes can disrupt productivity and academic performance.
- Physical health: Individuals with bipolar disorder are at increased risk for other medical conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
- Financial stability: Bipolar disorder can impact earning potential and lead to financial instability due to job loss or impulsive spending during manic episodes.
Nursing Care Plan for Bipolar Disorder
A comprehensive nursing care plan for bipolar disorder aims to:
- Stabilize mood episodes: This involves medication management, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Promote coping skills: Teaching strategies for managing stress, improving emotional regulation, and maintaining healthy habits.
- Educate the patient and family: Providing comprehensive information about the condition, its treatment, and support resources.
- Reduce risk of harm: Assessing for suicidal ideation and implementing measures to ensure patient safety.
Nursing Interventions:
Specific nursing interventions that can be implemented in a care plan for bipolar disorder include:
- Assessment and monitoring of mood: Regularly assess the patient’s mood, behavior, and any changes in their mental state.
- Medication administration and education: Administer medications as prescribed and educate the patient on the purpose and potential side effects of their medications.
- Psychotherapy and counseling: Encourage participation in individual or group therapy, which provides tools for managing emotions, improving communication, and developing coping mechanisms.
- Safety planning: Implement safety plans for individuals at risk of suicide or self-harm, including identifying support systems and strategies for managing crisis situations.
- Promote sleep hygiene: Encourage consistent sleep schedules, relaxation techniques, and avoidance of stimulants before bedtime.
- Encourage healthy lifestyle changes: Advise on maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and limiting alcohol and drug use.
- Family education and support: Provide information and support to family members to help them understand the condition and how to best support their loved one.
Latest Trends and Developments
The field of mental health is constantly evolving, and research on bipolar disorder continues to uncover new insights and therapies. Recent trends and developments include:
- Personalized medicine: Emerging research focuses on tailoring treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup and brain chemistry. This personalized approach aims to optimize medication effectiveness and minimize side effects.
- Digital mental health technologies: Apps and online platforms are being used to provide support, medication reminders, and access to mental health resources.
- Integrative approaches: Combining conventional therapies with complementary interventions such as mindfulness, yoga, and acupuncture is gaining increasing popularity.
- Increased awareness and destigmatization: Efforts to raise awareness about mental health conditions, including bipolar disorder, are helping to reduce stigma and encourage individuals to seek help.
Tips and Expert Advice
For Patients and Families
Living with bipolar disorder can be challenging, but there are strategies that can help manage the condition and improve quality of life.
- Learn about bipolar disorder: Gaining an understanding of the condition can help you manage expectations and navigate treatment decisions.
- Follow your treatment plan: Consistency with medications, therapy, and healthy lifestyle habits is essential for stabilizing mood episodes.
- Identify and avoid triggers: Understanding what triggers mood swings can help you implement strategies to minimize their impact.
- Build a support network: Surround yourself with family, friends, or a support group who can provide understanding and encouragement.
- Practice self-care: Prioritize healthy eating, regular exercise, and adequate sleep to maintain physical and mental well-being.
For Nurses
Providing compassionate and effective care for patients with bipolar disorder requires specialized knowledge and skills. Key nursing considerations include:
- Empathy and understanding: Approach patients with compassion and understanding, recognizing the challenges they face.
- Open communication: Establish open communication to foster trust and encourage patients to share their feelings and concerns.
- Active listening: Pay close attention to patients’ descriptions of their symptoms, ensuring you fully understand their experiences.
- Treatment adherence: Promote adherence to medication regimens and therapy appointments.
- Safety monitoring: Maintain vigilance in assessing for suicidal ideation and implementing appropriate safety measures.
- Advocacy: Advocate for patients’ needs and support their access to appropriate resources and services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What causes bipolar disorder?
The exact cause of bipolar disorder is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that imbalances in certain brain chemicals, particularly neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, may play a role.
Q: Is there a cure for bipolar disorder?
While there is no cure for bipolar disorder, it is a highly treatable condition. Medications and therapy can significantly manage symptoms and help individuals live fulfilling lives.
Q: How is bipolar disorder diagnosed?
A diagnosis of bipolar disorder is typically made by a mental health professional based on a clinical evaluation, including a review of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history.
Q: What are the treatment options for bipolar disorder?
Treatment options for bipolar disorder typically involve a combination of medication and therapy. Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants may be prescribed to manage mood swings. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals develop coping skills and manage their condition.
Q: Can bipolar disorder be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent bipolar disorder, early intervention and support for individuals with mental health concerns can be crucial in mitigating risk factors and promoting recovery.
Nursing Care Plan For Bipolar Disorder
https://youtube.com/watch?v=YfKNYCRGHLo
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of bipolar disorder requires a comprehensive nursing care plan tailored to the individual’s needs. By understanding the different phases of the condition, the impact it has on daily life, and the essential nursing interventions, we can provide compassionate and effective care that empowers patients to manage their symptoms and live meaningful lives. This article has outlined key aspects of a nursing care plan for bipolar disorder, including medication management, psychotherapy, safety measures, and lifestyle modifications. By embracing a holistic approach, we can help individuals with bipolar disorder navigate the complexities of their condition while fostering hope and resilience.
Are you interested in learning more about bipolar disorder and its treatment? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below.




